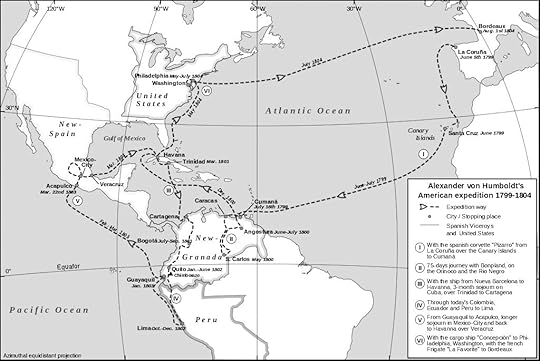
Having just finished reading Humboldt's COSMOS, and Andrea Wulf's "The Invention of Nature" about Humboldt, it seems time for me to read this before our Book Discussion Group turn's to the Wulf biography in the middle of August. I have this treat ahead of me.
To begin, this Gutenberg version has been somewhat condensed according to the persons converting it digitally from the 1907 British edition of this publication. Humboldt's Personal Narratives of South America was published in three volumes. The entire Volume One is what Project Gutenberg provided and which I finished. This edition translated from the French and edited by Thomasina Ross.
TRANSLATOR AND EDITOR's Introduction: "Prior to the travels of Alexander Von Humboldt and Aime Bonpland, the countries described in the following narrative were but imperfectly known to Europeans. For our partial acquaintance with them we were chiefly indebted to the early navigators, and to some of the followers of the Spanish Conquistadores. The intrepid men whose courage and enterprise prompted them to explore unknown seas for the discovery of a New World, have left behind them narratives of their adventures, and descriptions of the strange lands and people they visited, which must ever be perused with curiosity and interest; and some of the followers of Pizarro and Cortez, as well as many learned Spaniards who proceeded to South America soon after the conquest, were the authors of historical and other works of high value. But these writings of a past age, however curious and interesting, are deficient in that spirit of scientific investigation which enhances the importance and utility of accounts of travels in distant regions. In more recent times, the researches of La Condamine tended in a most important degree to promote geographical knowledge; and he, as well as other eminent botanists who visited the coasts of South America, and even ascended the Andes, contributed by their discoveries and collections to augment the vegetable riches of the Old World. But, in their time, geology as a science had little or no existence. Of the structure of the giant mountains of our globe scarcely anything was understood; whilst nothing was known beneath the earth in the New World, except what related to her mines of gold and silver. It remained for Humboldt to supply all that was wanting, by the publication of his Personal Narrative. In this, more than in any other of his works, he shows his power of contemplating nature in all her grandeur and variety."
HUMBOLDT'S PURPOSE IN THIS TRIP, as he states in his introduction: "I had in view a two-fold purpose in the travels of which I now publish the historical narrative. I wished to make known the countries I had visited; and to collect such facts as are fitted to elucidate a science of which we as yet possess scarcely the outline, and which has been vaguely denominated Natural History of the World, Theory of the Earth, or Physical Geography. The last of these two objects seemed to me the most important. I was passionately devoted to botany and certain parts of zoology, and I flattered myself that our investigations might add some new species to those already known, both in the animal and vegetable kingdoms; but preferring the connection of facts which have been long observed, to the knowledge of insulated facts, although new, the discovery of an unknown genus seemed to me far less interesting than an observation on the geographical relations of the vegetable world, on the migrations of the social plants, and the limit of the height which their different tribes attain on the flanks of the Cordilleras.
The natural sciences are connected by the same ties which link together all the phenomena of nature. The classification of the species, which must be considered as the fundamental part of botany, and the study of which is rendered attractive and easy by the introduction of natural methods, is to the geography of plants what descriptive mineralogy is to the indication of the rocks constituting the exterior crust of the globe. To comprehend the laws observed in the position of these rocks, to determine the age of their successive formations, and their identity in the most distant regions, the geologist should be previously acquainted with the simple fossils which compose the mass of mountains, and of which the names and character are the object of [uncomparable] knowledge. It is the same with that part of the natural history of the globe which treats of the relations plants have to each other, to the soil whence they spring, or to the air which they inhale and modify. The progress of the geography of plants depends in a great measure on that of descriptive botany; and it would be injurious to the advancement of science, to attempt rising to general ideas, whilst neglecting the knowledge of particular facts."
ATLANTIC CURRENTS INFORM EUROPEANS. Here is a quote from this first chapter. "deposits every year on the western coasts of Ireland and Norway the fruit of trees which belong to the torrid zone of America. On the shores of the Hebrides, we collect seeds of Mimosa scandens, of Dolichos urens, of Guilandina bonduc, and several other plants of Jamaica, the isle of Cuba, and of the neighbouring continent. The current carries thither also barrels of French wine, well preserved, the remains of the cargoes of vessels wrecked in the West Indian seas. To these examples of the distant migration of the vegetable world, others no less striking may be added. The wreck of an English vessel, the Tilbury, burnt near Jamaica, was found on the coast of Scotland. On these same coasts are sometimes found various kinds of tortoises, that inhabit the waters of the Antilles. When the western winds are of long duration, a current is formed in the high latitudes, which runs directly towards east-south-east, from the coasts of Greenland and Labrador, as far as the north of Scotland. Wallace relates, that twice (in 1682 and 1684), American savages of the race of the Esquimaux, driven out to sea in their leathern canoes, during a storm, and left to the guidance of the currents, reached the Orkneys. This last example is the more worthy of attention, as it proves at the same time how, at a period when the art of navigation was yet in its infancy, the motion of the waters of the ocean may have contributed to disseminate the different races of men over the face of the globe."
FACTS HUMBOLDT REPORTS IN THIS BOOK. "Those who have for a long time inhaled the air of the sea suffer every time they land; not because this air contains more oxygen than the air on shore, as has been erroneously supposed, but because it is less charged with those gaseous combinations, which the animal and vegetable substances, and the mud resulting from their decomposition, pour into the atmosphere. Miasms that escape chemical analysis have a powerful effect on our organs, especially when they have not for a long while been exposed to the same kind of irritation."
CANARY ISLANDS: "We must not be surprised that, previous to the time of Aristotle, we find no accurate notion respecting the Canary Islands and the volcanoes they contain, among the Greek geographers. The only nation whose navigations extended toward the west and the north, the Carthaginians, were interested in throwing a veil of mystery over those distant regions. While the senate of Carthage was averse to any partial emigration, it pointed out those islands as a place of refuge in times of trouble and public misfortune; they were to the Carthaginians what the free soil of America has become to Europeans amidst their religious and civil dissensions.
The Canaries were not better known to the Romans till eighty-four years before the reign of Augustus. A private individual was desirous of executing the project, which wise foresight had dictated to the senate of Carthage. Sertorius, conquered by Sylla, and weary of the din of war, looked out for a safe and peaceable retreat. He chose the Fortunate Islands, of which a delightful picture had been drawn for him on the shores of Baetica. He carefully combined the notions he acquired from travellers; but in the little that has been transmitted to us of those notions, and in the more minute descriptions of Sebosus and Juba, there is no mention of volcanoes or volcanic eruptions. Scarcely can we recognise the isle of Teneriffe, and the snows with which the summit of the Peak is covered in winter, in the name of Nivaria, given to one of the Fortunate Islands. Hence we might conclude, that the volcano at that time threw out no flames, if it were allowable so to interpret the silence of a few authors, whom we know only by short fragments or dry nomenclatures. The naturalist vainly seeks in history for documents of the first eruptions of the Peak; he nowhere finds any but in the language of the Guanches, in which the word Echeyde denotes, at the same time, hell and the volcano of Teneriffe.
Of all the written testimonies, the oldest I have found in relation to the activity of this volcano dates from the beginning of the sixteenth century. It is contained in the narrative of the voyage of Aloysio Cadamusto, who landed at the Canaries in 1505. This traveller was witness of no eruptions, but he positively affirms that, like Etna, this mountain burns without interruption, and that the fire has been seen by christians held in slavery by the Guanches of Teneriffe. The Peak, therefore, was not at that time in the state of repose in which we find it at present."
FLYING FISH- "f the sea covered with flying-fish,* (* Exocoetus volitans.) which threw themselves up into the air, twelve, fifteen, or eighteen feet, and fell down on the deck. I do not hesitate to speak on a subject of which voyagers discourse as frequently as of dolphins, sharks, sea-sickness, and the phosphorescence of the ocean. None of these topics can fail to afford interesting observations to naturalists, provided they make them their particular study. Nature is an inexhaustible source of investigation, and in proportion as the domain of science is extended, she presents herself to those who know how to interrogate her, under forms which they have never yet examined. I have named the flying-fish, in order to direct the attention of naturalists to the enormous size of their natatory bladder, which, in an animal of 6.4 inches, is 3.6 inches long, 0.9 of an inch broad, and contains three cubic inches and a half of air. As this bladder occupies more than half the size of the fish, it is probable that it contributes to its lightness. We may assert that this reservoir of air is more fitted for flying than swimming; for the experiments made by M. Provenzal and myself have proved, that, even in the species which are provided with this organ, it is not indispensably necessary for the ascending movement to the surface of the water. In a young flying-fish, 5.8 inches long, each of the pectoral fins, which serve as wings, presented a surface to the air of 3 7/16 square inches. We observed, that the nine branches of nerves, which go to the twelve rays of these fins, are almost three times the size of the nerves that belong to the ventral fins. When the former of these nerves are excited by galvanic electricity, the rays which support the membrane of the pectoral fin extend with five times the force with which the other fins move when galvanised by the same metals. Thus, the fish is capable of throwing itself horizontally the distance of twenty feet before retouching the water with the extremity of its fins. This motion has been aptly compared to that of a flat stone, which, thrown horizontally, bounds one or two feet above the water. Notwithstanding the extreme rapidity of this motion, it is certain, that the animal beats the air during the leap; that is, it alternately extends and closes its pectoral fins. The same motion has been observed in the flying scorpion of the rivers of Japan: they also contain a large air-bladder, with which the great part of the scorpions that have not the faculty of flying are unprovided. The flying-fish, like almost all animals which have gills, enjoy the power of equal respiration for a long time, both in water and in air, by the same organs; that is, by extracting the oxygen from the atmosphere as well as from the water in which it is dissolved. They pass a great part of their life in the air; but if they escape from the sea to avoid the voracity of the Dorado, they meet in the air the Frigate-bird, the Albatross, and others, which seize them in their flight. Thus, on the banks of the Orinoco, herds of the Cabiai, which rush from the water to escape the crocodile, become the prey of the jaguar, which awaits their arrival.
I doubt, however, whether the flying-fish spring out of the water merely to escape the pursuit of their enemies. Like swallows, they move by thousands in a right line, and in a direction constantly opposite to that of the waves. In our own climates, on the brink of a river, illumined by the rays of the sun, we often see solitary fish fearlessly bound above the surface as if they felt pleasure in breathing the air. Why should not these gambols be more frequent with the flying-fish, which from the strength of their pectoral fins, and the smallness of their specific gravity, can so easily support themselves in the air? I invite naturalists to examine whether other flying-fish, for instance the Exocoetus exiliens, the Trigla volitans, amid the T. hirundo, have as capacious an air-bladder as the flying-fish of the tropics. This last follows the heated waters of the Gulf-stream when they flow northward. The cabin-boys amuse themselves with cutting off a part of the pectoral fins, and assert, that these wings grow again; which seems to me not unlikely, from facts observed in other families of fishes."
PUBLISHER'S BRIEF: One of the greatest nineteenth-century scientist-explorers, Alexander von Humboldt traversed the tropical Spanish Americas between 1799 and 1804. By the time of his death in 1859, he had won international fame for his scientific discoveries, his observations of Native American peoples and his detailed descriptions of the flora and fauna of the 'new continent'. The first to draw and speculate on Aztec art, to observe reverse polarity in magnetism and to discover why America is called America, his writings profoundly influenced the course of Victorian culture, causing Darwin to reflect: 'He alone gives any notion of the feelings which are raised in the mind on first entering the Tropics'.