Art Lovers discussion
Architecture of the Ages
>
Architecture of the Renaissance
date newest »
newest »
 newest »
newest »


Tempietto di San Pietro in Montorio, Rome, 1502, by Bramante. This small temple marks the place where St Peter was put to death.
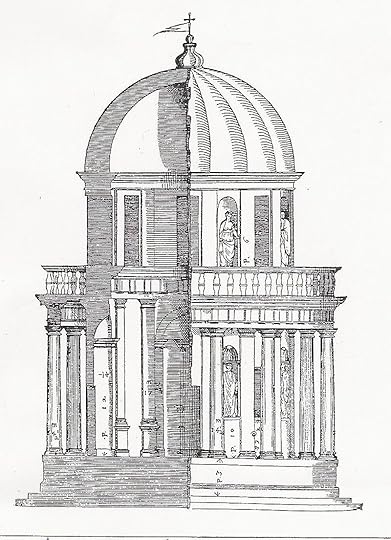
Palladio's engraving of Bramante's Tempietto
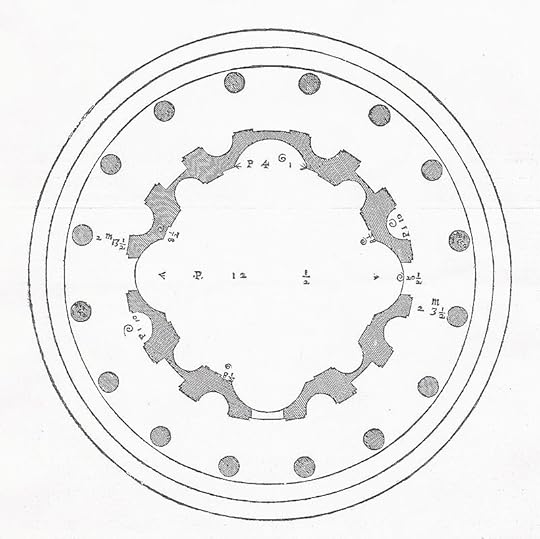
Plan of Bramante's Tempietto in Montorio
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renaiss....


Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower
Brunelleschi's Dome, the nave, and Giotto's Campanile of the Cattedrale di Santa Maria del Fiore as seen from Michelangelo Hill at night.
The cathedral begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally completed by 1436, with the dome designed by Filippo Brunelleschi. The exterior of the basilica is faced with polychrome marble panels in various shades of green and pink, bordered by white, and has an elaborate 19th-century Gothic Revival façade by Emilio De Fabris.
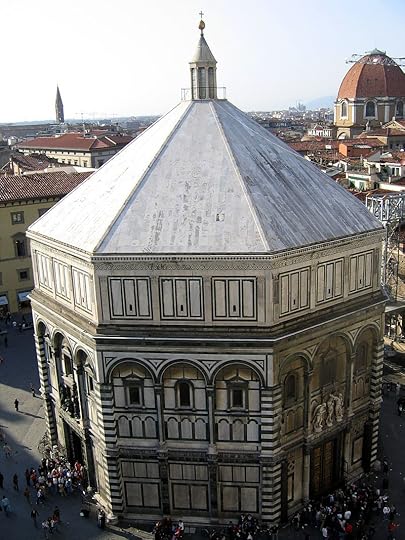
The cathedral complex, in Piazza del Duomo, includes the Baptistery and Giotto's Campanile. These three buildings are part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site covering the historic centre of Florence and are a major tourist attraction of Tuscany. The basilica is one of Italy's largest churches, and until the development of new structural materials in the modern era, the dome was the largest in the world. It remains the largest brick dome ever constructed.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Florenc...
 Brunelleschi's Dome
Brunelleschi's Dome
By the beginning of the 15th century, after a hundred years of construction, the structure was still missing its dome. The basic features of the dome had been designed by Arnolfo di Cambio in 1296. His brick model, 4.6 metres (15.1 feet) high, 9.2 metres (30.2 feet) long, was standing in a side aisle of the unfinished building, and had long been sacrosanct.[16] It called for an octagonal dome higher and wider than any that had ever been built, with no external buttresses to keep it from spreading and falling under its own weight.
The commitment to reject traditional Gothic buttresses had been made when Neri di Fioravanti's model was chosen over a competing one by Giovanni di Lapo Ghini.[18] That architectural choice, in 1367, was one of the first events of the Italian Renaissance, marking a break with the Medieval Gothic style and a return to the classic Mediterranean dome. Italian architects regarded Gothic flying buttresses as ugly makeshifts. Furthermore, the use of buttresses was forbidden in Florence, as the style was favored by central Italy's traditional enemies to the north.[19] Neri's model depicted a massive inner dome, open at the top to admit light, like Rome's Pantheon, but enclosed in a thinner outer shell, partly supported by the inner dome, to keep out the weather. It was to stand on an unbuttressed octagonal drum. Neri's dome would need an internal defense against spreading (hoop stress), but none had yet been designed.
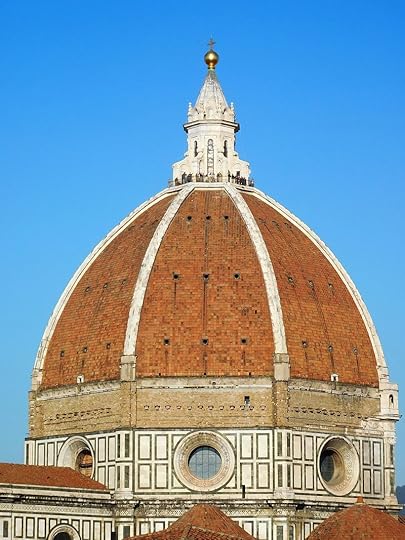

The building of such a masonry dome posed many technical problems. Brunelleschi looked to the great dome of the Pantheon in Rome for solutions. The dome of the Pantheon is a single shell of concrete, the formula for which had long since been forgotten. The Pantheon had employed structural centring to support the concrete dome while it cured [20]. This could not be the solution in the case of a dome this size and would put the church out of use. For the height and breadth of the dome designed by Neri, starting 52 metres (171 ft) above the floor and spanning 44 metres (144 ft), there was not enough timber in Tuscany to build the scaffolding and forms.[21] Brunelleschi chose to follow such design and employed a double shell, made of sandstone and marble. Brunelleschi would have to build the dome out of brick, due to its light weight compared to stone and being easier to form, and with nothing under it during construction. To illustrate his proposed structural plan, he constructed a wooden and brick model with the help of Donatello and Nanni di Banco, a model which is still displayed in the Museo dell'Opera del Duomo. The model served as a guide for the craftsmen, but was intentionally incomplete, so as to ensure Brunelleschi's control over the construction.
Brunelleschi's solutions were ingenious. The spreading problem was solved by a set of four internal horizontal stone and iron chains, serving as barrel hoops, embedded within the inner dome: one at the top, one at the bottom, with the remaining two evenly spaced between them. A fifth chain, made of wood, was placed between the first and second of the stone chains. Since the dome was octagonal rather than round, a simple chain, squeezing the dome like a barrel hoop, would have put all its pressure on the eight corners of the dome. The chains needed to be rigid octagons, stiff enough to hold their shape, so as not to deform the dome as they held it together.
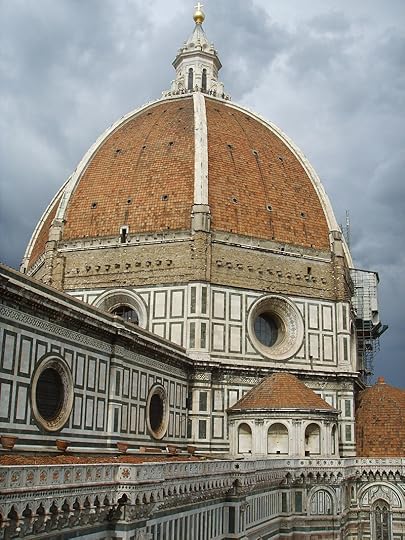

Each of Brunelleschi's stone chains was built like an octagonal railroad track with parallel rails and cross ties, all made of sandstone beams 43 centimetres (17 in) in diameter and no more than 2.3 metres (7.5 ft) long. The rails were connected end-to-end with lead-glazed iron splices. The cross ties and rails were notched together and then covered with the bricks and mortar of the inner dome. The cross ties of the bottom chain can be seen protruding from the drum at the base of the dome. The others are hidden. Each stone chain was supposed to be reinforced with a standard iron chain made of interlocking links, but a magnetic survey conducted in the 1970s failed to detect any evidence of iron chains, which if they exist are deeply embedded in the thick masonry walls. Brunelleschi also included vertical "ribs" set on the corners of the octagon, curving towards the center point. The ribs, 4 metres (13 ft) deep, are supported by 16 concealed ribs radiating from center. The ribs had slits to take beams that supported platforms, thus allowing the work to progress upward without the need for scaffolding.
A circular masonry dome can be built without supports, called centering, because each course of bricks is a horizontal arch that resists compression. In Florence, the octagonal inner dome was thick enough for an imaginary circle to be embedded in it at each level, a feature that would hold the dome up eventually, but could not hold the bricks in place while the mortar was still wet. Brunelleschi used a herringbone brick pattern to transfer the weight of the freshly laid bricks to the nearest vertical ribs of the non-circular dome.
The outer dome was not thick enough to contain embedded horizontal circles, being only 60 centimetres (2 ft) thick at the base and 30 centimetres (1 ft) thick at the top. To create such circles, Brunelleschi thickened the outer dome at the inside of its corners at nine different elevations, creating nine masonry rings, which can be observed today from the space between the two domes. To counteract hoop stress, the outer dome relies entirely on its attachment to the inner dome and has no embedded chains.

Interior of the dome
A modern understanding of physical laws and the mathematical tools for calculating stresses were centuries in the future. Brunelleschi, like all cathedral builders, had to rely on intuition and whatever he could learn from the large scale models he built. To lift 37,000 tons of material, including over 4 million bricks, he invented hoisting machines and lewissons for hoisting large stones. These specially designed machines and his structural innovations were Brunelleschi's chief contribution to architecture. Although he was executing an aesthetic plan made half a century earlier, it is his name, rather than Neri's, that is commonly associated with the dome.
Brunelleschi's ability to crown the dome with a lantern was questioned and he had to undergo another competition, even though there had been evidence that Brunelleschi had been working on a design for a lantern for the upper part of the dome. The evidence is shown in the curvature, which was made steeper than the original model. He was declared the winner over his competitors Lorenzo Ghiberti and Antonio Ciaccheri. His design (now on display in the Museum Opera del Duomo) was for an octagonal lantern with eight radiating buttresses and eight high arched windows. Construction of the lantern was begun a few months before his death in 1446. Then, for 15 years, little progress was possible, due to alterations by several architects. The lantern was finally completed by Brunelleschi's friend Michelozzo in 1461. The conical roof was crowned with a gilt copper ball and cross, containing holy relics, by Verrocchio in 1469. This brings the total height of the dome and lantern to 114.5 metres (376 ft). This copper ball was struck by lightning on 17 July 1600 and fell down. It was replaced by an even larger one two years later.
The commission for this gilt copper ball [atop the lantern] went to the sculptor Andrea del Verrocchio, in whose workshop there was at this time a young apprentice named Leonardo da Vinci. Fascinated by Filippo's [Brunelleschi's] machines, which Verrocchio used to hoist the ball, Leonardo made a series of sketches of them and, as a result, is often given credit for their invention.
Leonardo might have also participated in the design of the bronze ball, as stated in the G manuscript of Paris "Remember the way we soldered the ball of Santa Maria del Fiore".
The decorations of the drum gallery by Baccio d'Agnolo were never finished after being disapproved by no one less than Michelangelo.
A huge statue of Brunelleschi now sits outside the Palazzo dei Canonici in the Piazza del Duomo, looking thoughtfully up towards his greatest achievement, the dome that would forever dominate the panorama of Florence. It is still the largest masonry dome in the world.
The building of the cathedral had started in 1296 with the design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was completed in 1469 with the placing of Verrochio's copper ball atop the lantern. But the façade was still unfinished and would remain so until the 19th century.
 Renaissance Architecture and Its Influence
Renaissance Architecture and Its Influence
by Jackie Craven
The Renaissance describes an era from roughly 1400 to 1600 AD when art and architectural design returned to the Classical ideas of ancient Greece and Rome. In large part, it was a movement spurred on by the advances in printing by Johannes Gutenberg in 1440. The wider dissemination of Classical works, from the ancient Roman poet Virgil to the Roman architect Vitruvius, created a renewed interest in the Classics and a humanist way of thinking that broke with long-standing medieval notions.
This "age of "awakening" in Italy and northern Europe became known as the Renaissance, which means born anew in French. The Renaissance in European history left behind the Gothic era; it was a new way for writers, artists, and architects to look at the world after the Middle Ages. In Britain, it was the time of William Shakespeare, a writer who seemed to be interested in everything; art, love, history, and tragedy. In Italy, the Renaissance flourished with artists of innumerable talents.
Before the dawn of the Renaissance, Europe was dominated by asymmetrical and ornate Gothic architecture. During the Renaissance, however, architects were inspired by the highly symmetrical and carefully proportioned buildings of Classical Greece and Rome.
 Features of Renaissance Buildings
Features of Renaissance BuildingsThe influence of Renaissance architecture is still felt today in a more contemporary home. Consider that the common Palladian window* originated in Italy during the Renaissance. Other characteristic features of the era's architecture include:
-Symmetrical arrangement of windows and doors
-Extensive use of columns of the Classical orders and pilasters
-Triangular pediments
-Square lintels
-Arches
-Domes
-Niches with sculptures
*Palladian window: Pal·la·di·an win·dow
a large window consisting of a central arched section flanked by two narrow rectangular sections.

 Phases of Renaissance Architecture
Phases of Renaissance ArchitectureArtists in northern Italy were exploring new ideas for centuries before the period we call the Renaissance. However, the 1400s and 1500s brought an explosion of talent and innovation. Florence, Italy is often considered the center of the Early Italian Renaissance. During the early 1400s, the painter and architect Filippo Brunelleschi (1377-1446) designed the great Duomo (cathedral) dome in Florence (c. 1436), so innovative in design and construction that even today it's called Brunelleschi's Dome. The Ospedale degli Innocenti (c. 1445), a children's hospital also in Florence, Italy, was one of Brunelleschi's first designs.
Brunelleschi also rediscovered the principles of linear perspective, which the more refined Leon Battista Alberti (1404 to 1472) examined further and documented. Alberti, as a writer, architect, philosopher, and poet, became known as the true Renaissance Man of many skills and interests. His design of the Palazzo Rucellai (c. 1450) is said to be "truly divorced from the medieval style, and could finally be considered quintessentially Renaissance:" Alberti's books on painting and architecture are considered classics to this day.
 What is called the "High Renaissance" was dominated by the works of Leonardo da Vinci (1452 to 1519) and the young upstart Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475 to 1564). These artists built on the works of those who came before them, extending a classical brilliance that is admired to this day.
What is called the "High Renaissance" was dominated by the works of Leonardo da Vinci (1452 to 1519) and the young upstart Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475 to 1564). These artists built on the works of those who came before them, extending a classical brilliance that is admired to this day.Leonardo, famous for his paintings of "The Last Supper" and the "Mona Lisa", continued the tradition of what we call the "Renaissance Man." His notebooks of inventions and geometrical sketches, including the "Vitruvian Man", remain iconic. As an urban planner, like the ancient Romans before him, da Vinci spent his last years in France, planning a Utopian city for the King.
During the 1500s, the great Renaissance master, the radical Michelangelo Buonarroti, painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel and designed the dome for St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican. Michelangelo's most recognizable sculptures are arguably the "Pieta" and the grand 17-foot marble statue of "David" The Renaissance in Europe was a time when art and architecture were inseparable and the skills and talents of a single man could change the course of culture. Often talents worked together under Papal direction.
 Lasting Influences of Renaissance Architects
Lasting Influences of Renaissance ArchitectsA Classical approach to architecture spread through Europe, thanks to books by two important Renaissance architects.
Originally printed in 1562, the Canon of the Five Orders of Architecture by Giacomo da Vignola (1507 to 1573) was a practical textbook for the 16th-century builder. It was a "how-to" pictorial description for building with different types of Greek and Roman columns. As an architect Vignola had a hand in St. Peter's Basilica and the Palazzo Farnese in Rome, Villa Farnese, and other large country estates for the Catholic elite of Rome. Like other Renaissance architects of his time, Vignola designed with balusters, which became known as banisters in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Andrea Palladio (1508 to 1580) may have been even more influential than Vignola. Originally published in 1570, The Four Books of Architecture by Palladio not only described the five Classical Orders, but also showed with floor plans and elevation drawings how to apply the Classical elements to houses, bridges, and basilicas. In the fourth book, Palladio examines real Roman temples; local architecture like the Pantheon in Rome was deconstructed and illustrated in what continues to be a textbook of Classical design. Andrea Palladio's architecture from the 1500s still stands as some of the finest examples of Renaissance design and construction. Palladio's Redentore and San Giorigo Maggiore in Venice, Italy are not the Gothic sacred places of the past, but with columns, domes, and pediments they are reminiscent of Classical architecture. With the Basilica in Vicenza, Palladio transformed the Gothic remains of one building into what became a template for the Palladian window we know today. La Rotonda (Villa Capra) shown on this page, with its columns and symmetry and dome, became a template in years to come for a "new" Classical or "neo-classical" architecture worldwide.
As Renaissance approaches to building spread to France, Spain, Holland, Germany, Russia, and England, each country incorporated its own building traditions and created its own version of Classicism. By the 1600s, architectural design took another turn as ornate Baroque styles emerged and came to dominate Europe.
Long after the Renaissance period ended, however, architects were inspired by Renaissance ideas. Thomas Jefferson was influenced by Palladio and modeled his own home at Monticello on Palladio's La Rotonda. At the turn of the twentieth century, American architects like Richard Morris Hunt designed grand style homes that resembled palaces and villas from Renaissance Italy. The Breakers in Newport, Rhode Island may look like a Renaissance "cottage," but as it was built in 1895 it is Renaissance Revival.
If the Renaissance of Classical designs had not happened in the 15th and 16th centuries, would we know anything of ancient Greek and Roman architecture? Maybe, but the Renaissance sure makes it easier.
https://www.thoughtco.com/renaissance...




Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 14th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact.
Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts, as they are demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pilasters and lintels, as well as the use of semicircular arches, hemispherical domes, niches and aedicula replaced the more complex proportional systems and irregular profiles of medieval buildings.