Doctor Who and the Web of Fear, by Terrance Dicks
 Originally published on 19 August 1976, this is the first Doctor Who book issued from the new home of Wyndham Publications Ltd: 123 King Street in Hammersmith, London. The previous novelisations — and the three Mounties books — give the address of 14 Gloucester Road in South Kensington, the modest basement from which this whole industry started.
Originally published on 19 August 1976, this is the first Doctor Who book issued from the new home of Wyndham Publications Ltd: 123 King Street in Hammersmith, London. The previous novelisations — and the three Mounties books — give the address of 14 Gloucester Road in South Kensington, the modest basement from which this whole industry started.Beyond that one-line change in the indicia of this novelisation, which I doubt most readers noticed, there’s no evident sign of things being any different. The authoritative history on all this stuff, The Target Book, suggests that things were not happy at King Street, with a humber of staff leaving or losing their jobs, yet also quotes children’s editor Liz Godfray saying that,
“the Doctor Who schedule was largely unaffected by the behind the scenes changes” (David J Howe with Tim Neal, The Target Book (Telos, 2007) p. 34).
As we’ve seen in previous posts, the early days of Target saw delays in publication and titles being switched about. But by this point the range had reached what we might call a time of peace and ordered calm. We can see this in a list of forthcoming novelisations published in the fanzine TARDIS, vol 1, no. 8 (July 1976) and supplied by one Angus Towler in Cookridge — presumably a fan who had written into Target:
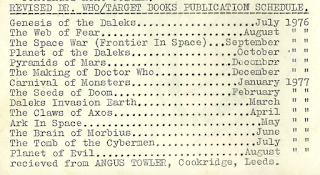
This is pretty much what got published over the next 12 months, with only Doctor Who and the Tomb of the Cybermen pushed back to a later date. The range was now a well-oiled machine. Keep cranking the handle and out came novelisations — plop, plop, plop.
If we apply my estimated lead time of 7.5 months, Terrance wrote Doctor Who and the Web of Fear in January 1976, while the Doctor Who story The Brain of Morbius was on air — a serial he wrote but asked to have his name taken off. Though Terrance seems to have been quick to forgive script editor Robert Holmes for rewriting his story so drastically, it had not been a happy experience. If current Doctor Who was not a source of joy, I wonder how much he took solace in returning to the first Doctor Who story with which he had a connection.
He didn’t work on the TV version of The Web of Fear. “When I first arrived [at the BBC]”, he told the Doctor Who Appreciation Society’s local group in Surbiton on 28 March 1978,
“that show was being edited, and I remember seeing playbacks of episode six.” (reported in the fanzine Oracle and reproduced in Stephen James Walker (ed.), Talkback — The Unofficial and Unauthorised Doctor Who Interview Book, Volume One: The Sixties (Telos, 2006), p. 179).
Episode 6 of The Web of Fear was recorded on Saturday, 17 February 1968 and broadcast on 9 March. There’s no surviving paperwork to tell us the date of this playback — which was when the edited, completed episode was shown to cast and crew in Theatre D at BBC Television Centre (with star Patrick Troughton invited to watch it upstairs, in the office of head of serials Shaun Sutton). I’ve discussed this with David Brunt, author of the forthcoming The Doctor Who Production Diary: The Troughton Years, and we think — based on earlier episodes of The Web of Fear for which records survive — that it was probably the Thursday after recording, i.e. 22 February.
This is significant because Terrance later claimed that he’d not really watched Doctor Who until he started working on it. So the date of the playback suggests he became a regular viewer from Episode 4 of The Web of Fear, broadcast on 24 February — having already seen Episode 6 in playback. Or, perhaps, knowing he was joining this series and would attend a screening of cast and crew, he tuned in the previous week and his first regular viewing of Doctor Who was Episode 3.
I like to think so, because — by coincidence — that episode saw the debut of Nicholas Courtney as Colonel Lethbridge-Stewart. Nick, like Terrance, joined Doctor Who for what he thought would be a matter of weeks, and by the end of the year had become part of the establishment of the TV series. They each remained regulars on the series until 1974 and 1975 respectively, and close to it ever after.
In fact, this long association caused a problem for Terrance in novelising The Web of Fear. When that story first aired, viewers didn’t know Lethbridge-Stewart at all. That he “suddenly popped out from nowhere” (says the Doctor), one of just two survivors of an attack by Yeti at Holborn, means we’re invited not to trust him. He is one of the characters we’re effectively invited to view as suspects — a potential servant of the alien Great Intelligence. The others include cowardly Driver Evans (the only other survivor from Holborn), supercilious journalist Howard Chorley, and salt-of-the-earth Mancunian, Staff Sergeant Arnold.
But most readers of the novelisation of Doctor Who and the Web of Fear would know the character of Lethbridge-Stewart from his subsequent adventures, in TV Doctor Who and in previously published novelisations. Terrance acknowledged this up front. In the TV version, little is made of the Doctor’s first meeting with Lethbridge-Stewart. In the book, we get this to open Chapter 5, putting this on a par with one of the most famous meetings of two men in British imperial history:
“Although neither of them realised it, this was in its way as historic an encounter as that between Stanley and Doctor Livingstone. Promoted to Brigadier, Lethbridge-Stewart would one day lead the British section of an organisation called UNIT (United Nations Intelligence Taskforce), set up to fight alien attacks on the planet Earth. The Doctor, changed in appearance and temporarily exiled to Earth, was to become UNIT’s Scientific Adviser.* But that was all in the future. For the moment, the two friends-to-be glared at each other in mutual suspicion.” (p. 42)
The asterisk links to a footnote, “See Doctor Who and the Auton Invasion”. It is Terrance linking the first Doctor Who story with which he had a connection to his first Doctor Who novelisation.
The reference in the above paragraph to the Doctor and Lethbridge-Stewart’s friendship being “all in the future” is also literally true. As per the scripts and broadcast version of The Web of Fear, we are told that the Doctor’s previous encounter with Yeti, in The Abominable Snowmen, took place in 1935 (p. 8 of this novelisation), which was “over forty years” (p. 8) before the events of this story; he includes a footnote, citing his novelisation.
The novelisation of The Web of Fear is therefore set, at the very earliest, in 1976 — the year it was published — meaning that all Lethbridge-Stewart’s subsequent adventures, as the Brigadier at UNIT, were still yet to take place. A young reader of this novelisation when it was published might have had dim memories of Lethbridge-Stewart’s second TV adventure, The Invasion, broadcast in 1968. For a 12 year-old, eight years ago is the ancient past. The young reader of this novelisation would have been presented with the boggling thought that it was also in the future.
Indeed, in Episode 2 of The Invasion, the Brigadier says the encounter with Yetis “in the Underground [ie in The Web of Fear] must be four years ago now”, meaning that The Invasion is set, at the earliest, in 1980. But just before Terrance started work on this novelisation, dialogue in the TV story Pyramids of Mars (broadcast 25 October — 15 November 1975) states — more than once — that Sarah Jane Smith is from “1980”, presumably meaning that the events in Terror of the Zygons take place in that year. That story was Lethbridge-Stewart’s last regular appearance on screen.
So all the Brigadier’s adventures, from The Invasion (1968) to Terror of the Zygons (1975), occur in a single calendar year. No wonder he had a breakdown…
*
My first edition of this novelisation is in pretty good nick, the cover still smooth and shiny, only the spine a bit creased. The cover illustration is among Chris Achilleos’s best. Instead of the usual black-and-white stippled portrait of the Doctor’s staring dolefully back at us, the second Doctor is in colour, his face expressive, agonised, looking downwards — as if under terrible pressure.
Behind him, radiating outwards to fill the frame, is a cobweb in black-on-white, which may explain the choice to put the Doctor in colour so he stands out. On some previous covers, Achilleos framed the central figure with radiating colours. The cobweb is much more effective, I think, because it is something tangible, not just a tone. Cobweb also has associations with horror, while the stark black and white is colder and less comforting that the colour fills.
The Doctor’s gaze directs our attention to the elements in the lower part of the frame: a Yeti with bright beams of energy blasting out from its eyes to ensnare a soldier. In fact, this is a bit of a spoiler because the ensnared soldier is Staff Sergeant Arnold, the character revealed at the climax of the story to be the servant of the baddies. Yet there’s nothing in the cover or the text of the book to identify that this is Arnold, beyond the stripes on his arm signifying his rank as sergeant.
I wonder if Achilleos even knew that the soldier he put on the cover was the bad guy in the story. It may be that he simply worked from the most dynamic stock photo available, a soldier brandishing a rifle rather than just standing around.
 Reference photo from The Web of Fear,
Reference photo from The Web of Fear, showing Jack Woolgar
as Staff Sergeant Arnold,
c/o the Black Archive
The beams of bright energy are edged with purple, which may have dictated — or been chosen so as to compliment — the purple Doctor Who logo. This is only the second purple logo featured in the range (following Doctor Who and the Tenth Planet), and the second time a Doctor Who novelisation featured a purple spine and back cover.

In fact, the back covers of this book and Doctor Who and the Doomsday Weapon (1974) look very similar. Both employ yellow text on purple. Using one of the three primary colours (blue, red or yellow) in juxtaposition with a colour mixed from the other two is a well-known technique, the clash of so-called “complimentary” colours meant to be striking and bright.

The difference between these two back covers is revealing about the way the range had changed in its first two years. Doctor Who and the Doomsday Weapon boasts a single paragraph in yellow teasing the plot of the book, the key characters and elements given capital letters. There’s then a quotation from a newspaper, underlining the universal appeal of Doctor Who — generally, not this particular story — to both children and adults. The slogan “A TARGET ADVENTURE”, places Doctor Who within a wider genre of exciting books (something John Grindrod first pointed out to me).
There’s no quotation or slogan on the back of Doctor Who and the Web of Fear, as though Doctor Who by now could stand on its own, with no need of introduction. The yellow-coloured text teasing the plot comprises fewer words than the earlier book (87 words compared to 97) but the point size is much bigger and the text presented in three paragraphs — the words less densely packed and so more digestible.
The novelisation is similarly digestible, six 25-minute episode condensed into just 128 pages, whereas Terrance’s previous novelisation needed 144. Last week, in response to my last post, Paul MC Smith from Wonderful Books produced this helpful graph of wordcounts:
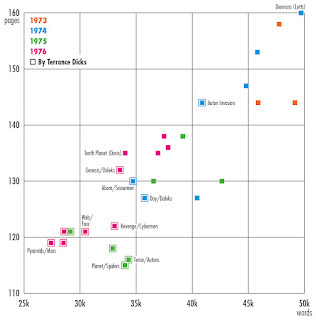 Relative word counts of Doctor Who novelisations
Relative word counts of Doctor Who novelisationsGraph by Paul MC Smith
To keep Doctor Who and the Web of Fear breezily concise, Terrance cut anything inessential to the plot, including visually arresting moments from the TV serial that don’t really suit prose. For example, the opening scene of Episode 1 picks up from the end of the previous serial, with the doors of the TARDIS wide open while the ship is still in flight, the Doctor and his friends at risk of tumbling out. Likewise, episode 4 of the TV version features a thrilling battle between Lethbridge-Stewart’s soldiers and the Yeti in the streets of Covent Garden. Both are missing from the book.
Otherwise, it’s a pretty faithful record of the story seen on screen, with some deft amendments. For example, the unfortunate stereotype of rich, greedy Julius Silverstein in the TV version is here a “tall, elegant white-hair old man”, Emil Julius, much more childish than grasping.
Terrance also picks up on the attempt by Captain Knight to chat up Anne Travers in episode 1, where she cuts him dead.
KNIGHT:
What’s a girl like you doing in a job like this?
ANNE TRAVERS:
Well, when I was a little girl I thought I’d like to be a scientist. So I became a scientist.
To this, Terrance adds that Knight, “welcomed any opportunity to work with Anne Travers” (p. 28), offering to help her with a task rather than send for a technician. It makes a bit more of their relationship, suggesting something more along the lines of that between Captain Turner and Isobel Watkins in The Invasion — where the characters end up together. Here, the relationship seems to be one way; when, later, Knight is killed by Yeti, there’s no suggestion that Anne spares him even a thought.
This is an example of an addition Terrance makes at the start of the story that doesn’t pay off at the end. Another is — as I said above — his telling us on p. 42 that Lethbridge-Stewart is someone we can trust when, on screen, he’s one of the characters we’re invited to suspect is one of the Great Intelligence’s suspects. Terrance sets up that guess-who-the-baddie-is early on; on p. 31 he reminds us of the Doctor’s previous encounter with the Yeti, and the Intelligence’s ability to take over and control unwitting human servants. As the story continues, on p. 70 he makes the guess-who plot explicit, the Doctor thinking through the six suspects by name: Anne Travers and her father, then Chorley, Lethbridge-Stewart, Knight and Arnold.
We know to discount Lethbridge-Stewart — we’re reminded, on p. 77, that this man and the Doctor are at the start of a long friendship. But in listing the suspects on p. 70, Terrance surely lays a false lead by not including a name: he leaves out Evans. This is just after he’s reminded us that Evans is cowardly and selfish, with Jamie appalled that the man refuses to do anything dangerous and would rather run away.
“Jamie shook his head. ‘I’m not running out on my friends.’
Evans stood up. “Well, I’m sorry to leave you, boyo, but you got to take care of number one in this world.’” (p. 66)
Again, Terrance is keen to avoid stereotypes, and later shares a thought from Lethbridge-Stewart — who we know we can trust — that “the Welsh usually made such splendid soldiers” (p. 99). Terrance also ensures that at the end of the story, Evans finds “unexpected resources of courage” (p. 91) and redeems his earlier shortcomings. The cowardly red-herring character ends the story as a hero.
The Doctor here is also a compassionate, considerate hero. He’s introduced vividly,
“a small man with untidy black hair and a gentle humorous face. He wore baggy check trousers and a disreputable frock coat” (p. 13).
Later, when he is “looting” an electronics shop in Goodge Street for the components he desperately needs to thwart the Intelligence and save everyone on Earth,
“At the back of his mind he hoped that the Government would remember to pay compensation [to the shop owner]” (p. 93).
At the end of the story, he wins the battle but not the war against the Intelligence because his friends have, with the best of intentions, tried to help. On screen, he is cross with them. Here, his anger is quickly curtailed by “seeing the happy faces all round him” (p. 124) and he asks for their forgiveness. It’s characteristic Terrance; it’s rare on screen for the Doctor to apologise. As in previous novelisations, Terrance makes the Doctor a bit kinder and more heroic. He also underlines that this is the same man as other incarnations, here using the Third Doctor’s catchphrase “reverse the polarity”.
Then there are the other regular characters. “Towering over” the Doctor, Jamie — no surname — is introduced to us as, “a brawny youth in Highland dress, complete with kilt”, who has been travelling in the TARDIS “since the Doctor’s visit to Earth at the time of the Jacobite rebellion” (p. 13). That background shapes Jamie’s character here in ways it doesn’t in the TV version, such as when he first encounters soldiers.
“Although their coats were khaki rather than red, Jamie found it hard to forget that English soldiers were his traditional enemies” (p. 45)
I wonder if that was informed by the complex relationships between redcoats and Indians in Terrance’s Mounties trilogy. But this kind of complex relationship between characters, each of whom thinks they are right, is characteristic of Terrance. Here, he adds that while the Doctor and Jamie are “the best of friends … occasional disputes were inevitable” (p. 13).
Victoria — no surname — is introduced as a “small, dark girl” (p. 14); as with Sarah in Terrance’s previous novelisations, the darkness refers to her hair, not her complexion. Again, we get a concise history of this character, an orphan from 19th century London. Sadly, this then doesn’t inform her actions in the story. Even so, Terrance adds a couple of interesting character moments for her not in the TV version, First, there’s her perspective on the young man in her life:
“Jamie had rushed off with his usual impulsiveness, forgetting all about her” (p. 48).
There’s no suggestion of romantic feelings or emotional connection between them, as was seen in the next TV story. Rather, Jamie doesn’t consider Victoria. Terrance does not add anything to pre-empt the events of that next TV story, such as suggesting that Victoria is in any way unhappy aboard the TARDIS. In fact, he adds something I think informed by his own interest at the time in meditation and positive thinking, when Victoria makes an effort to say something positive:
“Travers was still very confused and Victoria felt she had to keep his spirits up. Strangely enough this had the effect of making her feel better herself” (p. 105).
Then there’s Lethbridge-Stewart, introduced here as having an,
“immaculate uniform and a neatly trimmed moustache” … ‘And who might you be?’ he asked [the Doctor], sounding more amused than alarmed.” (p. 40)
“Amused” is such an apposite word to describe Nicholas Courtney’s manner of playing the character. Terrance also refers to the man’s “relaxed confidence” (p. 63), which is again very apt. Nicely, we glimpse how Lethbridge-Stewart sees the Doctor, as a “funny little chap” (p. 75), and then get the contrary view with the Doctor recognising a soldier who knows no surrender (p. 76). Indeed, that’s an issue for Lethbridge Stewart, trained for action yet in a situation where he is unable to act (p. 90). In spelling this out, Terrance makes action the consequence of character.
We’re told Lethbridge’Stewart’s name is Alastair (p. 41), the name first used in print in The Making of Doctor Who (1972), cowritten by Terrance, and on screen in Planet of the Spiders (1974), script-edited by Terrance. Terrance still doesn’t use the middle name “Gordon”, for all it was used on screen in Robot (1974-5), which he wrote. As I’ve said before, that suggests “Gordon” was an ad lib by Tom Baker in rehearsals on that story, to improve the rhythm of the character’s name. But it also suggests that the various fans in contact with the publisher and with Terrance by the time he was writing the novelisation hadn’t pointed out the missing part of the name.
That interaction with fans had a big impact on Terrance’s approach to these novelisations. We’re on the cusp of that change here. Between writing this book in January 1976 and it being published in August, Terrance received a letter from fan Richard Landen listing continuity errors in The Making of Doctor Who, and was a guest at a DWAS meeting at Westfield College, University of London. Reading up on this interactions, I’m struck by Terrance’s patience in dealing with fans in their late teens and 20s expressing the view that books written for 8 to 12 year-olds are perhaps a bit childish…
This tiresome fan could point out odd things in Doctor Who and the Web of Fear, the stuff I might pick up if I were editing this book. Just as the Doctor makes an unwitting cameo in one of the Mounties books because Terrance wrote the word with a capital D, Captain Knight refers here to “some kind of Doctor” and “the Doctor who was in the tunnels” (both p. 36) before he knows it’s the character’s name. In the same vein, why does Lethbridge Stewart need to tell his men that they’re looking for a “blue Police Box” (p. 89) — if they know what a police box is at all, they’d surely know it was blue.
I would be tempted to excuse such pendantry by saying it’s a living. But it doesn’t really pay.
Still, this journeyman writer is enthralled by how deftly Terrance adapts the TV story. The scripts were brilliantly, vividly conveyed by director Douglas Camfield. It’s a hard task to relay anything of the same atmosphere in prose, but Terrance is brilliantly vivid. Mostly, he tells us directly what’s happening so we can easily visualise each scene. He doesn’t embellish or overly complicate the action, but makes things more palpable through his choice of words.
For example, there’s the Yeti dragging the unconscious old Travers, “as a child drags a teddy bear by one arm” (p. 81) — perfectly, simply, conveying the gait of toddling creature, the prey hanging limp in its grasp, the relative power of these two bodies. He adds bits of army slang to convey the culture and feel of these soldiers — “bodge” (p. 86), “spit and polish” (p. 111), and “daftie” (p. 119). And then there’s another example of his sophisticated vocabulary in a book aimed at children, which makes perfect sense in context, when the Doctor responds to “Jamie’s woebegone face” (p. 99).
At the end of the novelisation, Terrance sets up what’s to come in the lore of Doctor Who, with Lethbridge Stewart telling Travers that this adventure has shown the need for some kind of intelligence Taskforce.
“I think I’ll send the Government a memorandum…” (p. 125)
This archivist of all-things Doctor Who is delighted to think that UNIT began with a memo. (What was the subject line? To whom was it CC’d? What were the initials in the bottom left, a clue to the name of Lethbridge Stewart’s secretary?)
With his memo, we know — not least because Terrance told us in opening Chapter 5 — that everything is about to change in the world of Doctor Who. And yet the book closes on what are by now stock phrases in Terrance’s books, Doctor Who the same as it ever was and will be. With a “wheezing, ground sound”, the TARDIS fades from view.
“The Doctor and his two companions were ready to begin their next adventure” (p. 126)
*
These long posts on the 236 books written by Terrance Dicks take time and effort. and involve expenses. I don’t currently have enough other paid work to justify going on with them without your support.
kofiwidget2.init('Support me on Ko-fi', '#72a4f2', 'H2H2COHMI');kofiwidget2.draw();Throw some coins in the hat and next week you get Doctor Who and the Planet of the Daleks. And then we’re onto Christmas 1976 and the triple whammy of The Making of Doctor Who (and the origins of “never cruel or cowardly”), Doctor Who and the Pyramids of Mars (about which Terrance discussed his working methods), and The Doctor Who Dinosaur Book (I’ve been talking to palaeontologists)…
Simon Guerrier's Blog
- Simon Guerrier's profile
- 60 followers



